Placement
Mix laydown involves everything used to place the delivered HMA on the desired surface at the desired thickness. The asphalt paver is the principal machine involved in mix laydown and is assisted by the material transfer vehicle (MTV) in some instances.
 |
 |
| Figure 1: Asphalt paver. | Figure 2: HMA placement. |
Video 1: SMA Placement at Hilo Harbor
Placement Considerations
There are, of course, many considerations to take into account when placing HMA. Many are dependent upon local materials, weather, crew knowledge and training, and individual experience. This subsection presents a few of the basic considerations that apply in virtually all situations:
- Lift thickness. A "lift" refers to a layer of pavement as placed by the asphalt paver. In order to avoid mat tearing (which generally shows up as a series of longitudinal streaks) a good rule-of-thumb is that the depth of the compacted lift should be at least twice the maximum aggregate size and three times the nominal maximum aggregate size (TRB, 2000).
| HAPI Pavement Note on Lift Thickness |
Lift thickness plays an important role in both HMA compaction and final mat smoothness. Lifts thinner than three times the nominal maximum aggregate size are difficult to compact because there is simply not enough room for the aggregate particles to rearrange within the lift as it is compacted. HDOT uses a method specification rather than an end-result specification on lift thicknesses less than 1.5 inches for this reason. Overly thick final lifts have a tendency to shove or displace during compaction making it difficult to achieve a smooth finish. Generally, for a State mix IV a good final lift thickness that is compactable but will not shove excessively is about 2 inches. |
- Longitudinal joints. The interface between two adjacent and parallel HMA mats. Improperly constructed longitudinal joints can cause premature deterioration of multilane HMA pavements in the form of cracking and raveling.
- Handwork. HMA can be placed by hand in situations where the
paver cannot place it adequately. This can often occur around
utilities, around intersection corners and in other tight spaces.
Hand-placing should be minimized because it is prone to aggregate
segregation and results in a slightly rough surface texture.
If hand placement is necessary the following precautions should
be taken (Asphalt Institute, 2001):
- Place the HMA in a pile far enough away from the placement area that the whole pile must be moved. If the pile is located in the placement area its appearance, density or aggregate distribution may be slightly different than the surrounding handworked mat.
- Carefully deposit the material with shovels and then spread with lutes. Do not broadcast (scoop and pitch) the HMA with shovels - this is likely to cause aggregate segregation.
- All material should be thoroughly loosened and evenly distributed. Chunks of HMA that do not easily break apart should be removed and discarded.
- Check the handworked surface with a straightedge or template before rolling to ensure uniformity.
Asphalt Paver
The asphalt paver is a self-propelled formless (does not require side forms) laydown machine with a floating screed (see Figures 1, 2, 3 and 4). HMA is loaded in the front, carried to the rear by a set of flight feeders (conveyor belts), spread out by a set of augers, then leveled and compacted by a screed. This set of functions can be divided into two main systems:
- Tractor. The tractor contains the material feed system, which accepts the HMA at the front of the paver, moves it to the rear and spreads it out to the desired width in preparation for screed leveling and compaction. The tractor moves using rubber tires (see Figures 1 and 2) or tracks (see Figure 3).
- Screed. The most critical feature of the paver is the self-leveling screed unit, which determines the profile of the HMA being placed (Roberts et al., 1996). The screed takes the head of HMA from the material delivery system, strikes it off at the correct thickness and provides initial mat compaction. Figure 5 shows screed components and the six basic forces that act upon the screed to determine its height and, thus, pavement thickness.

Figure 3: Tracked paver.
Figure 4: Paver schematic animation.
Figure 5: Screed components and forces.
Factors Affecting Mat Thickness and Smoothness
Since the screed is free floating it will slide across the HMA at an angle and height that will place the six forces shown in Figure 5 in equilibrium. When any one of these forces is changed, the screed angle and elevation will change (which will change the mat thickness) to bring these forces back into equilibrium. Therefore, changing the following paver characteristics will affect these forces, and thus mat thickness, in the described manner:
- Paver speed. If a paver speeds up and all other forces on the screed remain constant, the screed angle decreases to restore equilibrium, which decreases mat thickness (think of what happens to the ski angle of a water skier as boat speed increases).
- Material head. If the material head (the amount of material in front of the screed) increases (either due to an increase in material feed rate or a reduction in paver speed), screed angle will increase to restore equilibrium, which increases mat thickness.
- Tow point elevation. As the tow point rises in elevation, the screed angle increases, resulting in a thicker mat. As a rule-of-thumb, a 1-inch movement in tow point elevation translates to about a 0.125 inch movement in the screed's leading edge. Without automatic screed control, tow point elevation will change as tractor elevation changes due to roughness in the surface over which it drives. Locating the screed tow point near the middle of the tractor significantly reduces the transmission of small elevation changes in the front and rear of the tractor to the screed. Because the screed elevation responds slowly to changes in screed angle, the paver naturally places a thinner mat over high points in the existing surface and a thicker mat over low points in the existing surface (TRB, 2000).
- Screed angle can also be adjusted manually by using a thickness control screw or depth crank. Screed angle adjustments do not immediately change mat thickness but rather require a finite amount of time and tow distance to take effect. Figure 6 shows that it typically takes five tow lengths (the length between the tow point and the screed) after a desired level is input for a screed to arrive at the new level. Because of this screed reaction time, a screed operator who constantly adjusts screed level to produce a desired mat thickness will actually produce an excessively wavy, unsmooth pavement.
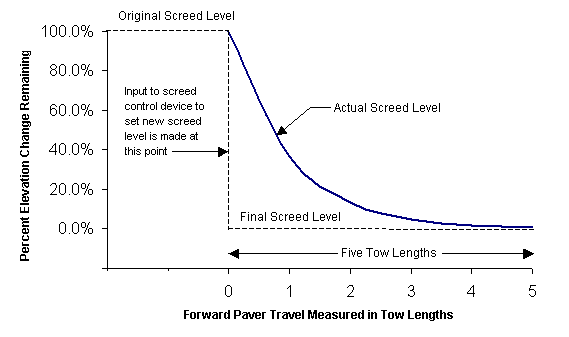
Figure 6: Screed Reaction to a Manual Decrease in Screed Angle (after TRB, 2000)
Automatic Screed Control
Since it is not practical to manually control tow point elevation, pavers usually operate using an automatic screed control, which controls tow point elevation using a reference other than the tractor body. Since these references assist in controlling HMA pavement grade, they are called “grade reference systems” and are listed below (Roberts et al., 1996):
- Erected stringline. This consists of stringline erected to specified elevations that are independent of existing ground elevation (see Figure 7). Most often this is done using a survey crew and a detailed elevation/grade plan. Although the stringline method provides the correct elevation (to within surveying and erecting tolerances), stringlines are fragile and easily broken, knocked over or inadvertently misaligned. Lasers can be used to overcome the difficulties associated with stringlines because they do not require any fragile material near the pavement construction area. Lasers can establish multiple elevation or grade planes even in dusty or high-electronic and light-noise areas and are therefore sometimes used to construct near-constant elevation airport runways. Even the laser method becomes quite complicated, however, when frequent pavement grade changes are required.
- Mobile reference. This consists of a reference system that travels with the paver such as a long beam or tube attached to the paver (called a "contact" device since it actually touches the road) or an ultrasonic device (called a "non-contact" device since it relies on ultrasonic pulses and not physical contact to determine road elevation - see Figure 8). The mobile reference system averages the effect of deviations in the existing pavement surface over a distance greater that the wheelbase of the tractor unit. Minimum ski length for a contact device is normally about 25 ft. with typical ski lengths being on the order of 40 to 60 ft. (Asphalt Institute, 2001).
- Joint matching shoe. This usually consists of a small shoe or ski attached to the paver that slides on an existing surface (such as a curb) near the paver. Ultra sonic sensors accomplish the same task without touching the existing surface by using sound pulses to determine elevation. This type of grade control results in the paver duplicating the reference surface on which the shoe or ski is placed or ultra sonic sensor is aimed.
 |
 |
| Figure 7: Stringline | Figure 8: Mobile Reference System (Circled) |
Material Transfer Vehicles (MTVs)
| HAPI Pavement Note on MTVs |
HDOT requires the use of an MTV when placing any main traffic lane HMA surface course. Hawai'i essentially does not use bottom dump trucks or windrows for paving. |
Material transfer vehicles (MTVs) are used to assist the paver in accepting HMA. Most pavers are equipped to receive HMA directly from end dump or live bottom trucks, however in certain situations it can be necessary or advantageous to use an MTV. Paving using bottom dump trucks and windrows requires a windrow elevator MTV, while other MTVs are used to provide additional surge volume, which is advantageous because it allows the paver to operate continuously without stopping, minimizes truck waiting time at the paving site and may minimize aggregate segregation and temperature differentials (see Figures 9 and 10).
 |
 |
| Figures 9 and 10: Roadtec Shuttlebuggy™ MTV. | |
Video 2: HMA Placement Using a Shuttlebuggy™ MTV.


